| Shipping Type | Order By |
|---|---|
|
Standard Ground Small Parcel FREE - On orders over $25 View Transit Map |
7:00 PM CST |
|
Next Day Air (Calculated at checkout) |
3:00 PM CST |
|
Standard Ground Freight FREE - On orders over $25 |
1:00 PM CST |
- Shipping cutoff times apply to in-stock items. Please note item lead-times when placing your order.
- Orders placed on weekends or holidays will be processed the next business day.
| Shipping Type | Order By |
|---|---|
|
Standard Ground Small Parcel FREE - On orders over $25 View Transit Map |
7:00 PM CST |
|
Next Day Air (Calculated at checkout) |
3:00 PM CST |
|
Standard Ground Freight FREE - On orders over $25 |
1:00 PM CST |
- Shipping cutoff times apply to in-stock items. Please note item lead-times when placing your order.
- Orders placed on weekends or holidays will be processed the next business day.
- Greenheck /
- Inline Fans /
- CSP-A

CSP-A
Performance Filter
Calculate Air Exchange (CFM)
Use the calculator to determine the Air Exchange (CFM) required to adequately ventilate an area.Enter information into the fields below to calculate the required airflow per fan.
To calculate the CFM required to adequately ventilate an area, we divide the room volume by the appropriate “Minutes per Change” value.
Airflow (CFM) per Fan
Starred items represent required fields.
Calculate Static Pressure (SP)
Use the calculator to determine the amount of static pressure the fan must overcome.The pressure generated by fans in ductwork is typically very small. An accurate measurement of static presure is critical to proper fan selection however. Static pressure in fan systems is typically less than 2" SP, or 0.072 Psi.
* Starred items represent required fields.
Static Pressure Guidelines
Non-Ducted 0.05" to 0.20"
Ducted 0.20" to 0.40" per 100 feet of duct (assuming duct air velocity falls within 1,000 to 1,800 feet per minute)
Fittings 0.08" per fitting (elbow, register, grill, damper, louver, duct turn, etc.)
Kitchen Hood Exhaust 0.625" to 1.50"
Important: Static pressure requirements are significantly affected by the amount of make-up air supplied to an area. Insufficient make-up air will increase static pressure and reduce the amount of air that will be exhausted. Remember, for each cubic foot of air exhausted, one cubic foot of air must be supplied.
| SKU | DRIVE TYPE | HP | VOLTAGE | MOTOR PHASE | CFM RANGE | FRPM RANGE | INLET WIDTH x HEIGHT | OUTLET WIDTH x HEIGHT | PRICE | LEAD TIME | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A250
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 82-266 | 800-1000 | 12 7/8 x 10 in | 8 x 8 in | $372.00 |
In stock
1178 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A410
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 217-447 | 800-1000 | 16 7/8 x 13 1/4 in | 8 x 8 in | $463.00 |
In stock
322 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A710
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 334-737 | 864-1080 | 16 7/8 x 13 1/4 in | 10 x 8 in | $703.00 |
In stock
340 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A710
|
Direct Drive | 1/4 | 120 | 1 | 350-737 | 400-1450 | 16 7/8 x 13 1/4 in | 10 x 8 in | $1,307.00 |
In stock
156 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A900
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 631-908 | 760-950 | 22 5/8 x 13 1/4 in | 17 7/16 x 8 in | $1,027.00 |
In stock
95 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A1050
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 752-1244 | 876-1095 | 22 5/8 x 13 1/4 in | 17 7/16 x 8 in | $1,027.00 |
In stock
161 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A1550
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 999-1672 | 1288-1610 | 22 5/8 x 13 1/4 in | 17 7/16 x 8 in | $1,136.00 |
In stock
75 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A700
|
Direct Drive | - | - | 1 | 100-801 | 1275-1450 | 22 5/8 x 10 1/2 in | 19 1/2 x 8 in | $1,350.00 |
In stock
245 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A390
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 281-412 | 1080-1350 | 12 7/8 x 10 in | 8 x 8 in | $435.00 |
In stock
749 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A200
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 70-254 | 720-900 | 12 7/8 x 10 in | 8 x 8 in | $372.00 |
In stock
1092 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A780
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 527-813 | 1280-1600 | 16 7/8 x 13 1/4 in | 10 x 8 in | $703.00 |
In stock
141 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A510
|
Direct Drive | 1/6 | 115 | 1 | 250-545 | 400-1275 | 16 7/8 x 13 1/4 in | 8 x 8 in | $1,259.00 |
In stock
107 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A510
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 325-545 | 856-1070 | 16 7/8 x 13 1/4 in | 8 x 8 in | $562.00 |
In stock
252 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A125
|
Direct Drive | - | 115 | 1 | 91-138 | 880-1100 | 11 7/8 x 7 5/8 in | 8 x 6 in | $313.00 |
In stock
718 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
|
|
Model:
CSP-A
Model / Size:
CSP-A390-VG
|
Direct Drive | - | 115/208-230 277 |
1 | 57-417 | 350-1750 | 12 7/8 x 10 in | 8 x 8 in | $676.00 |
In stock
538 on Hand
|
Add to Compare List |
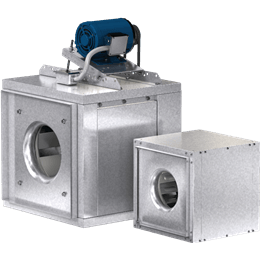
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A250-QD, 82-266 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 12.875 x 10 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A410-QD, 217-447 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 16.875 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A710-QD, 334-737 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 16.875 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 10 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A710-VG-QD, 350-737 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel and energy efficient, adjustable Vari-Green EC motors.
- 16.875 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 10 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Energy-efficient, speed controllable, Vari-green® motor
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A900-QD, 631-908 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 22.625 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 17.4375 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A1050-QD, 752-1244 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 22.625 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 17.4375 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A1550-QD, 999-1672 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 22.625 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 17.4375 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A700-VG-QD, 100-801 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel and an energy efficient, adjustable Vari-Green EC motor.
- 22.625 x 10.5 inch inlet width x height
- 19.5 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Energy-efficient, speed controllable, Vari-green® motor
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A390-QD, 281-412 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 12.875 x 10 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A200-QD, 70-254 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 12.875 x 10 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A780-QD, 527-813 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 16.875 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 10 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A510-VG-QD, 250-545 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel and an energy efficient, adjustable Vari-Green EC motor.
- 16.875 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Energy-efficient, speed controllable, Vari-green® motor
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A510-QD, 325-545 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 16.875 x 13.25 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 8 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Product # CSP-A125-QD, 91-138 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel.
- 11.875 x 7.625 inch inlet width x height
- 8 x 6 inch outlet width x height
- Speed controllable, with up to 30% turndown
Inline Cabinet Fan, Model CSP-A390-VG, 115/208-230/277V, 1 Ph, 57-417 CFM
Model CSP inline fans are high performance fans designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound level are required. Units feature an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved wheel. Model CSP-A390-VG features a tri-voltage design to operate at 115/208-230/277V. Vari-Green EC motor technology included for maximum fan controllability.
- Acoustic insulation absorbs sound for quiet operation
- Adjustable mounting brackets for multiple installation conditions
- Easy access to internal components through access panels
- Balance dial for system balancing
- Embossed, galvanized steel housing for rigidity
- Large electrical junction box for easy wiring
- Speed controllable motor
- Vertical electrical access to eliminate drilling holes
Shop Greenheck CSP-A
A direct drive, inline-mounted fan designed for exhaust, supply or return air applications where low sound levels are desired. The unit features an insulated, galvanized steel housing with a forward-curved centrifugal wheel. Ideal applications for this model are clean air including intake, exhaust, return or make-up air.Find by Performance
Our performance filter tool can help you choose the right product based on your performance requirements.
Filter Products
New Products, Deals, and More
Our experts are available Mon-Fri, 7am-5pm CT